
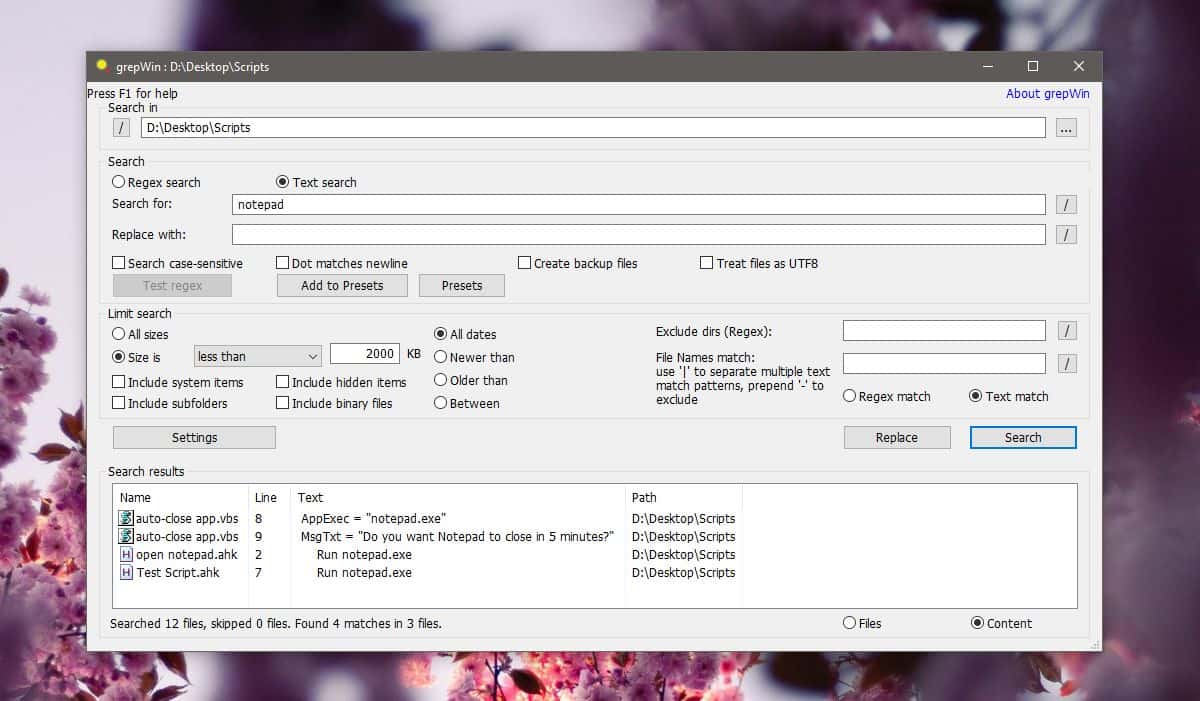
- #WINDOWS 10 HOW TO SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES INSTALL#
- #WINDOWS 10 HOW TO SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES FULL#
- #WINDOWS 10 HOW TO SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES WINDOWS 10#
You'll still be able to search by file name-just not file contents.Ĭhoosing not to index the contents of files can reduce the size of the index, but it makes files harder to find in some cases. For properties only, indexing will not look at the contents of the file or make the contents searchable. There are two options for how much of a file to index: either properties only, or properties and content. Can I change how much of a file's information is indexed? Which file types can be indexed?įor a list of file types that can be indexed, go to the Indexing Options control panel page and select Advanced > File Types. The index can take up a larger percentage if you have lots of very small files ( Time & Language > Region & language, and then select Add a language. For example, if you have 100 MB of text files, the index for those files will be less than 10 MB. How much space is used by the index?Ī rule of thumb is that the index will be less than 10 percent of the size of the indexed files.
#WINDOWS 10 HOW TO SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES INSTALL#
However, apps you install on your PC may be able to read the data in the index, so be careful with what you install and make sure you trust the source. None of it is sent to any other computer or to Microsoft. Where is the index information stored?Īll data gathered from indexing is stored locally on your PC.
To do this, it opens recently changed files, looks at the changes, and stores the new information in the index.
#WINDOWS 10 HOW TO SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES WINDOWS 10#
Your Windows 10 PC is constantly tracking changes to files and updating the index with the latest information. Why does indexing automatically run on my PC at all times? Disabling indexing will result in these apps either running slower or not working at all, depending on how heavily they rely on it. Many apps in the Microsoft Store also depend on the index to provide up-to-date search results for your files and other content. Cortana uses it to provide faster search results from across your PC. Microsoft Edge uses it to provide browser history results in the address bar. File Explorer, Photos, and Groove all use it to access and track changes to your files. Many of the built-in apps on your PC use the index in some way. For example, Outlook 2016 adds all emails synced to your machine to the index by default and uses the index for searching within the app. For files with text, their contents are indexed to allow you to search for words within the files.Īpps you install may also add their own information to the index to speed up searching.
#WINDOWS 10 HOW TO SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES FULL#
What information is indexed?īy default, all the properties of your files are indexed, including file names and full file paths.

A fully built index can return answers to searches such as "Show all songs by Coldplay" in a fraction of a second, versus the minutes it could take without an index. Much like having an index in a book, having a digital index allows your PC and apps to find content faster by looking for terms or common properties such as the date a file was created. How does indexing make my searches faster? After that, indexing will run in the background on your PC as you use it, only re-indexing updated data. When you first run indexing, it can take up to a couple hours to complete. When you search your PC after indexing, it looks at an index of terms to find results faster. Indexing is the process of looking at files, email messages, and other content on your PC and cataloging their information, such as the words and metadata in them. Indexing the contents of your PC helps you get faster results when you're searching it for files and other things.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
